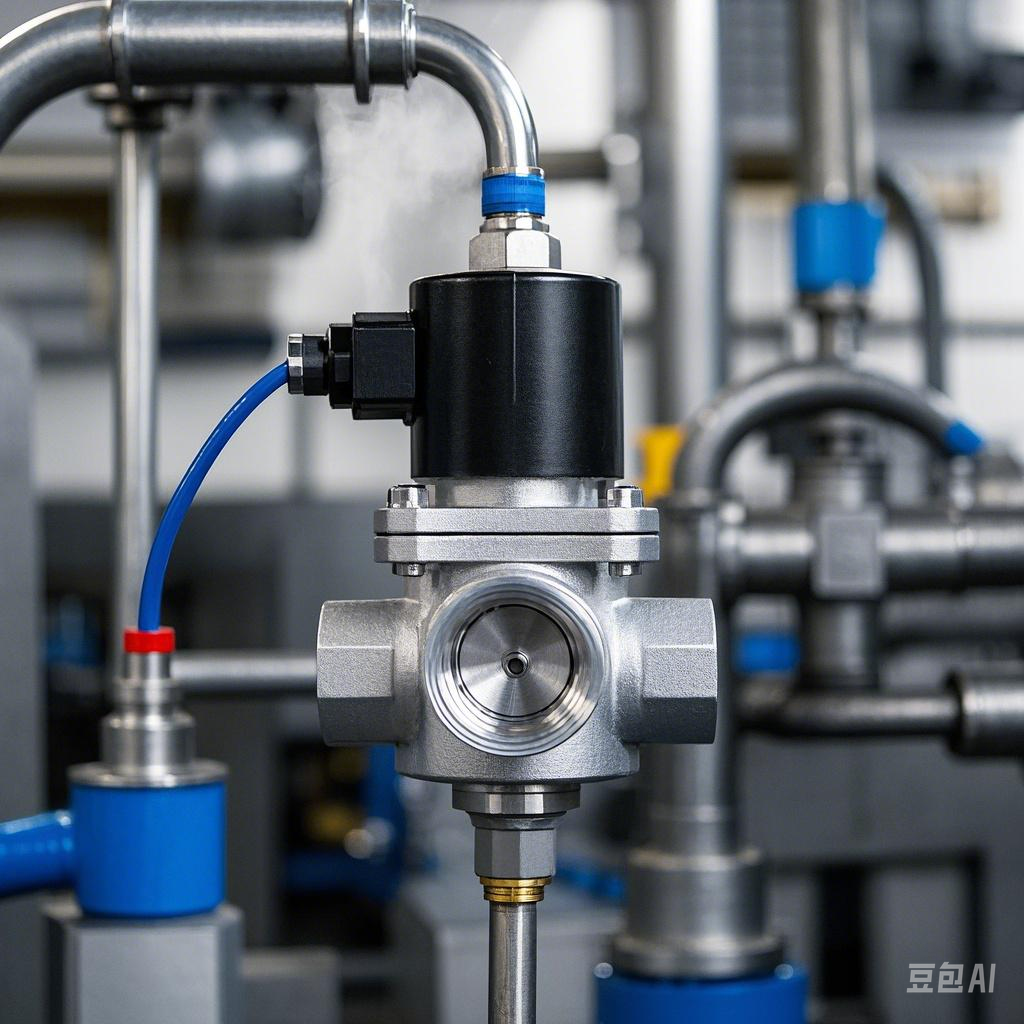
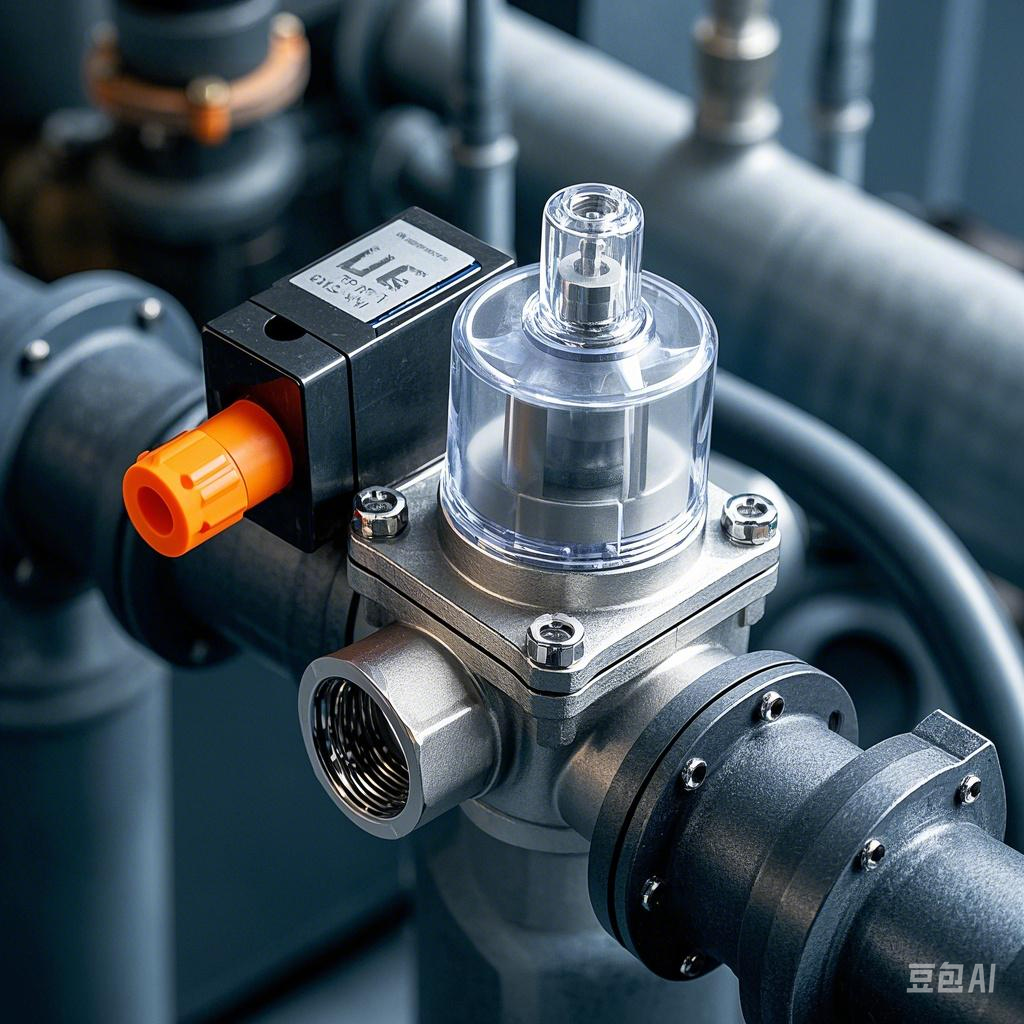
Solenoid valve, as a basic component in automation control, plays the role of actuator, widely used in mechanical control and industrial valve systems. Its main function is to control the direction of fluid flow, and then realize the precise manipulation of the valve switch.
Working Mechanism Revealed
The solenoid valve is equipped with a closed chamber, which has holes in different positions, each hole is connected to a different oil pipe. The center of the cavity is the valve body, and the valve body on each side of a solenoid. When the solenoid coil on one of the sides is energized, the valve body is attracted to that side. By controlling the movement of the valve body, different oil drain holes can be covered or exposed. It is important to note that the oil inlet holes are always open. As the hydraulic oil flows into the different discharge pipes, it uses oil pressure to push the piston of the cylinder into motion. The piston in turn drives the piston rod, which in turn drives the mechanism to perform the action. In this way, by controlling the current of the electromagnet, we can realize the precise control of mechanical movement.
Classification
Solenoid valves can be categorized in various ways, from the working principle can be divided into three main categories:
Direct-acting solenoid valve
Working principle: when energized, the electromagnetic force will open the pilot hole, so that the pressure of the upper chamber is rapidly reduced. In the valve body around the formation of an upper low high pressure difference, this pressure difference will push the valve body to move upward, so as to open the valve. In case of power failure, the spring force will close the pilot hole, and the pressure of the inlet will enter the chamber quickly through the bypass hole, forming a pressure difference around the valve body, which pushes the valve body to move downward and closes the valve.
Characteristics: able to work properly in vacuum, negative pressure or zero pressure environment, but the through diameter (i.e., the size of the valve opening) is generally not more than 25 mm.
Step-by-step direct-acting solenoid valve
Characteristics: Can work reliably even under zero differential pressure, vacuum or high pressure. However, they are more powerful and must be installed horizontally.
Pilot Operated Solenoid Valves
Characteristics: Capable of withstanding high fluid pressure ranges, they can be installed flexibly (customization required), but fluid differential pressure conditions must be met.
In addition, according to the structure and material of the valve body, as well as differences in the operating principle, solenoid valves can be further subdivided into six subcategories: direct diaphragm structure, step-by-step heavy-disk structure, pilot-operated diaphragm structure, direct-operated piston structure, step-by-step direct-operated piston structure, and pilot-operated piston structure.
In general, solenoid valves play an indispensable role in industrial automation control with their unique control mechanism and wide range of applications. No matter which type of solenoid valve, they all play a key role in their respective fields and promote the progress of industrial production.
What is the working principle of the solenoid valve what are the types of