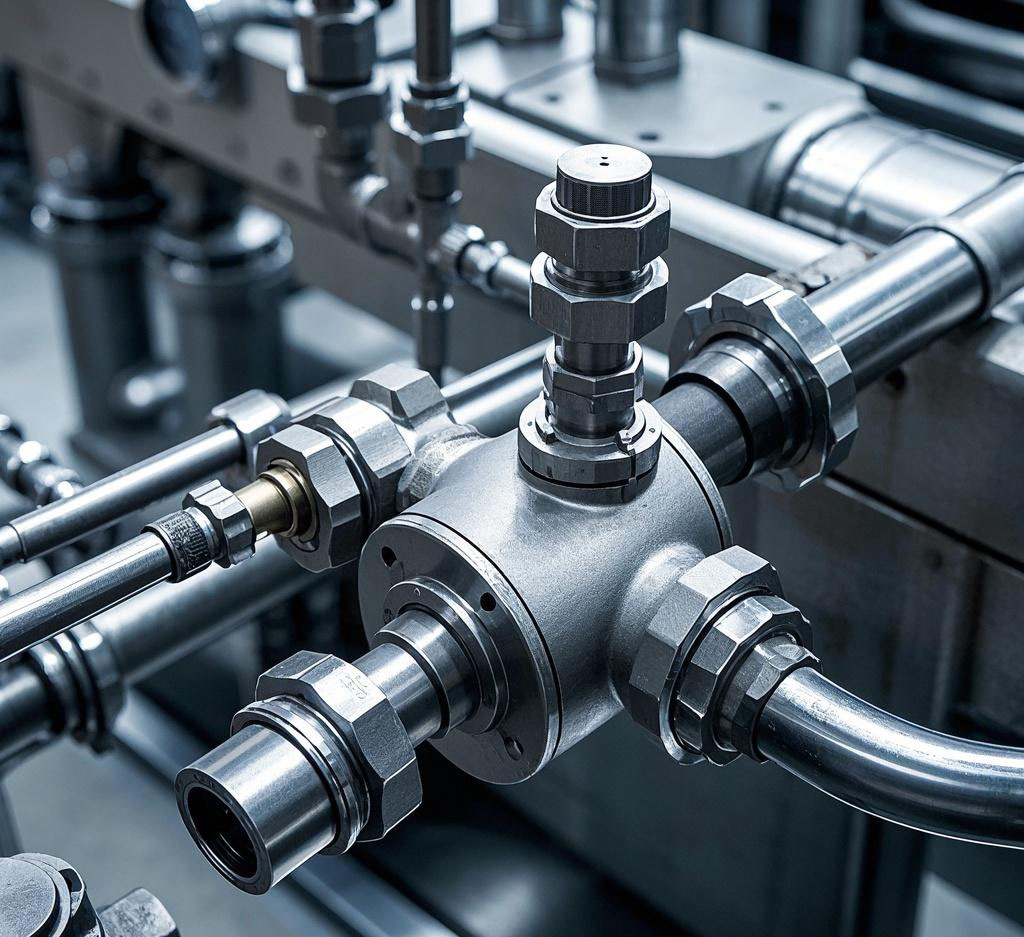
In the field of industry and construction, valves as an important component in the piping system, the quality of its installation is directly related to the future efficiency and safety of system operation. Therefore, it is crucial to know the correct way to install valves. The following is a detailed valve installation guide, designed to help engineers and construction personnel to easily understand and implement.
Valve installation five core points
- Orientation and Location Selection
Orientation Note: Many valves have a definite orientation, such as globe valves, throttle valves, pressure reducing valves and check valves. Installation of the reverse may lead to functional failure, shorten the life of the valve, and even cause safety hazards. Valves usually have directional markings on them, and if they are missing, they need to be correctly identified according to the principle of operation.
Convenient location: Valves should be installed in a location that is easy to operate, even if the initial installation is difficult, and the ease of long-term operation should be considered. Usually, the valve handwheel should be equivalent to the operator’s chest height (about 1.2 meters above the ground) to avoid operation on the back, especially when dealing with acid, alkali and toxic media. - Construction details
Inspection and preparation: Before installation, carefully check whether the valve model and specification are in accordance with the design requirements, check whether the packing is intact, whether the valve stem and disc are flexible and free of jams. Remove debris in the valve to ensure that the pipeline is clean.
Installation process: When lifting the valve, the rope should be tied to the flange to avoid damage to the handwheel or valve stem. When connecting the pipeline, make sure the flanges are parallel and the gap is reasonable, and tighten the bolts symmetrically and evenly. When welding the valves, spot weld first, then fully open and close the parts, and finally weld them. - Protective measures
Heat preservation and cold preservation: According to the characteristics of the medium and production requirements, the valve for heat preservation or cold preservation treatment. Insulation materials such as asbestos, slag cotton, etc., cold materials such as cork, foam, etc.. - Bypass and instrumentation configuration
Bypass setting: For critical valves, install bypass to facilitate maintenance. Whether to install bypass according to the valve status, importance and production needs to decide.
Instrumentation: According to the need, equip the valve with necessary instrumentation to monitor and control system operation. - Packing replacement
Suitable packing: according to the type of media to choose the appropriate packing, replacement to ensure that the packing is compacted uniformly, leaving a proper margin for adjustment.
Valve installation of fourteen taboos and precautions
Taboo 1: the use of materials and equipment without qualified certification.
Taboo 2: no quality inspection before installation.
Taboo 3: valve specifications do not meet the design requirements.
Taboo four: the installation method is wrong, such as reverse direction, improper location.
Taboo five: butterfly valve flange and ordinary valve flange mixing.
…… (the rest of the taboo omitted, can refer to the original text for similar rewriting)
Valve installation special reminders
Open-stem valves: avoid direct burial, should be installed in a covered trench or a convenient location for operation.
Handling and stacking: avoid throwing when the valve handling, stacking when classified storage to prevent deformation.
Operation space: to ensure that the valve is installed in a location convenient for operation and maintenance, set up a fixed operating platform or extension rod.
Directionality: according to the direction of media flow to determine the direction of valve installation, such as globe valve should be low into the high out.
Special requirements: familiar with the installation requirements of special valves, such as safety valves, pressure reducing valves.
Flange connection: ensure that the flange end face parallel, coaxial line, tighten the bolts using symmetrical or cross-crossing method.
Non-metallic valves: pay attention to light holding, avoid bumping, moderate opening and closing force during operation.
Conclusion
Valve installation is a critical part of ensuring the smooth operation of a piping system. By following the above guidelines, U.S. engineers and construction personnel can more efficiently and safely complete the valve installation work, laying a solid foundation for the long-term stable operation of the system. At the same time, regular inspection and maintenance is also an important measure to protect the performance of the valve and extend its service life.