Solenoid valves are core components of fluid control systems, acting as electromagnetic switches for gases, liquids and vapors. In this paper, we will analyze its core concept, operation mechanism and practical applications in industrial scenarios.
First, the key concept of solenoid valve
- Basic function
As a pilot valve or switching device, control pneumatic / hydraulic actuators.
Realize the precise passage or direction control of the fluid in the pipeline. - Classification standards
Category Example
Type of operation Direct-acting, pilot-operated, step-acting (combination of direct-acting and pilot-operated)
Port Configuration 2-position 2-way, 2-position 3-way, 2-position 4-way, 2-position 5-way (number of ports / number of spool positions)
Power supply type Alternating current (AC), Direct current (DC)
Fault position Normally open (NO), Normally closed (NC), Universal flow (non-latching)
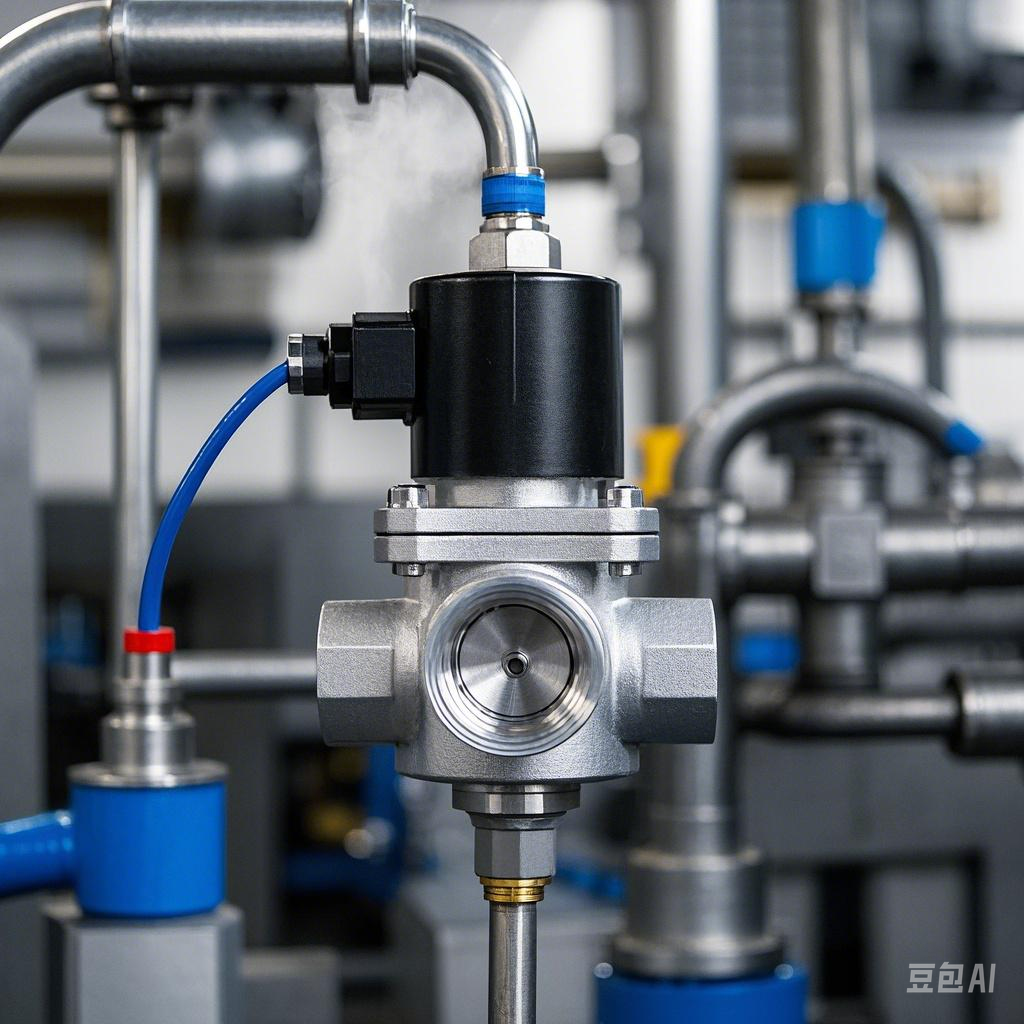
Second, the principle of work in detail - Direct-acting solenoid valve
Mechanism:
When the coil is energized, electromagnetic force is generated to lift the spool.
The spring pushes the spool to reset and close when the power is off.
Advantage:
Quick response (10-50ms).
No differential pressure required to operate. - Pilot Operated Solenoid Valve
Two stage process:
Pilot stage: the coil opens the pilot orifice and reduces the pressure in the upper chamber.
Main valve action: Differential pressure (lower chamber > upper chamber) pushes the main piston open.
Advantages:
Low power consumption for high flow control.
Suitable for large diameter piping systems. - Step-by-step direct-acting solenoid valves
Hybrid design:
Direct action at low pressure.
Switch to pilot mode after system pressurization.
Applicable Scenarios:
Need to balance the low-pressure start and high-flow performance of the system.
Core Application Scenarios
Process control
Gas/liquid flow regulation in chemical plants and food processing plants.
Safety Systems
Emergency shutdown valves (ESD) in oil and gas facilities.
Loss of power protection configurations (e.g. NC valves closed by power failure).
Automation
Control of pneumatic cylinders for robots and production lines.
Quick switches for sprinkler systems and HVAC equipment.
Selection Guide
Pressure Range: Match system pressure (e.g. 150 PSI vs. 1000 PSI).
Media compatibility: Select stainless steel, brass and other corrosion-resistant materials.
Response speed: need <50ms switching scene priority direct-acting type.
Summarize
Solenoid valve is a multi-faceted fluid control, from simple direct-acting to complex pilot-operated design. Mastering their principles and application scenarios ensures optimal performance of industrial automation systems. For customized solutions, contact a certified solenoid valve manufacturer for pressure testing and compatibility analysis.
Translated with DeepL.com (free version)