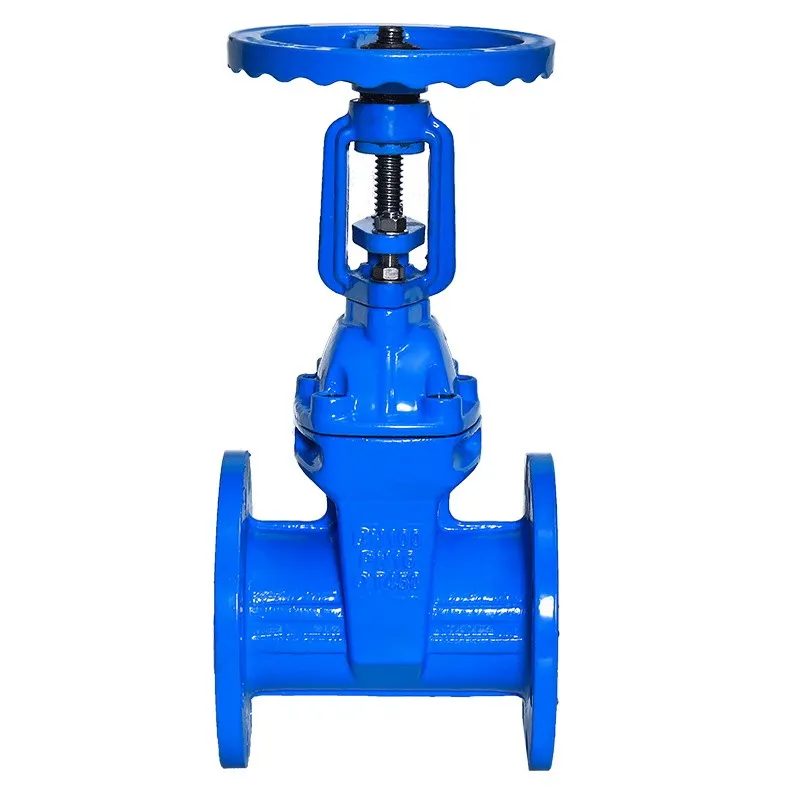
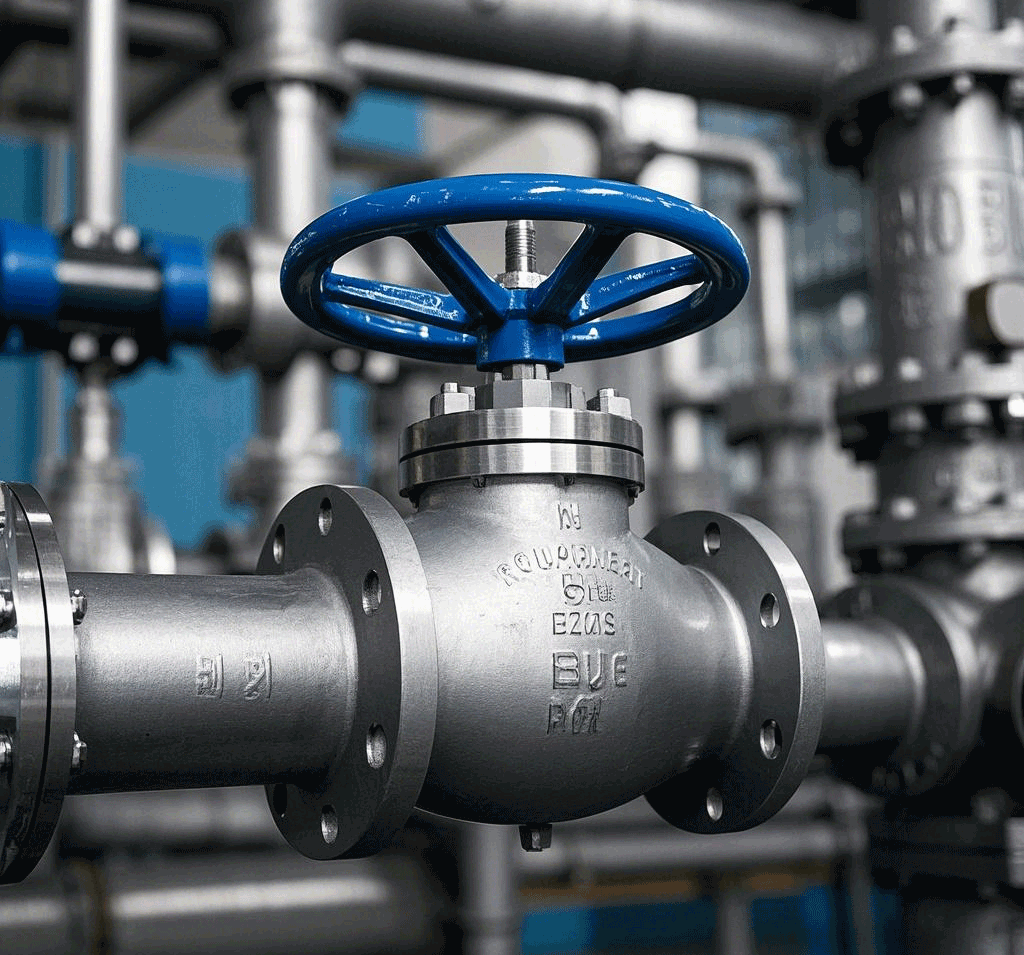
When installing and maintaining the gate valve, you need to pay attention to the following points:
First of all, the handwheel, handle and transmission mechanism are for manual operation only, and are strictly prohibited to be used as lifting tools and to avoid any kind of collision. For double-gate gate valves, ensure that they are installed vertically, i.e. the stem is in a vertical position and the handwheel is at the top. If the gate valve is equipped with a bypass valve, the bypass valve should be opened before the gate valve is formally opened to equalize the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet and to reduce the force required for opening. For gate valves with transmission mechanism, they should be installed in strict accordance with the product instruction manual.
If the gate valve needs to be opened and closed frequently, it is recommended to lubricate it at least once a month. Gate valves are mainly used to cut off the flow of media, when the valve is fully open, the fluid can pass through unimpeded, at this time the media pressure loss is minimized. Gate valves are usually suitable for working conditions that do not require frequent opening and closing, and the gate is kept fully open or fully closed. They are not suitable for regulating or throttling use, because of the high speed flow of the medium in the partial opening of the gate may cause vibration, which can damage the sealing surface of the gate and seat. Throttling may also lead to the gate by the media erosion.
From the structural form, the main difference between the gate valve is the sealing element used. According to the different sealing elements, the gate valve can be divided into a variety of types, such as wedge gate valve, parallel gate valve, parallel double gate gate valve and wedge double gate gate valve. Among them, wedge gate valve and parallel gate valve are the two most commonly used forms.
There is also a special type of valve – the check valve. The function of a check valve is to allow the medium to flow in one direction only and to prevent reverse flow. This type of valve usually works automatically, with the valve flap opening when the fluid flows in the permitted direction, and closing when the fluid flows in the opposite direction due to fluid pressure and its own weight, thus cutting off the flow. Check valves include swing check valves and lift check valves.
Swing-open check valves have a hinged mechanism where the valve flap rests freely against the sloping seat surface like a door. To ensure that the valve flap closes accurately, the flap is designed to have a certain amount of swing-open space for full contact with the seat. The valve flap can be made entirely of metal, or the metal can be inlaid with leather, rubber or other synthetic materials to meet different performance requirements. In the fully open state, the swing check valve is virtually unimpeded by fluid pressure, so the pressure drop through the valve is relatively small.
The flap of a lift check valve, on the other hand, sits on the seat sealing surface of the valve body. It is similar to a globe valve except that the valve flap is free to rise and fall. When fluid pressure lifts the valve flap from the seat sealing surface, the medium can flow; and when the medium flows back, the valve flap will fall back to the valve seat and cut off the flow. According to the conditions of use, the valve can be all-metal structure, can also be inlaid on the valve frame rubber gasket or rubber ring.
In the production process, in order to adjust the medium pressure, flow and other parameters to meet the requirements of the process, the need to install regulating agencies. The working principle of these regulators is to change the flow area between the valve flap and valve seat to achieve the purpose of regulating parameters. These valves are collectively referred to as control valves, which rely on the medium itself power-driven known as self-powered control valves (such as pressure reducing valves, pressure stabilizing valves, etc.), while relying on external power-driven known as his drive control valves (such as electric control valves, pneumatic control valves and hydraulic control valves, etc.).