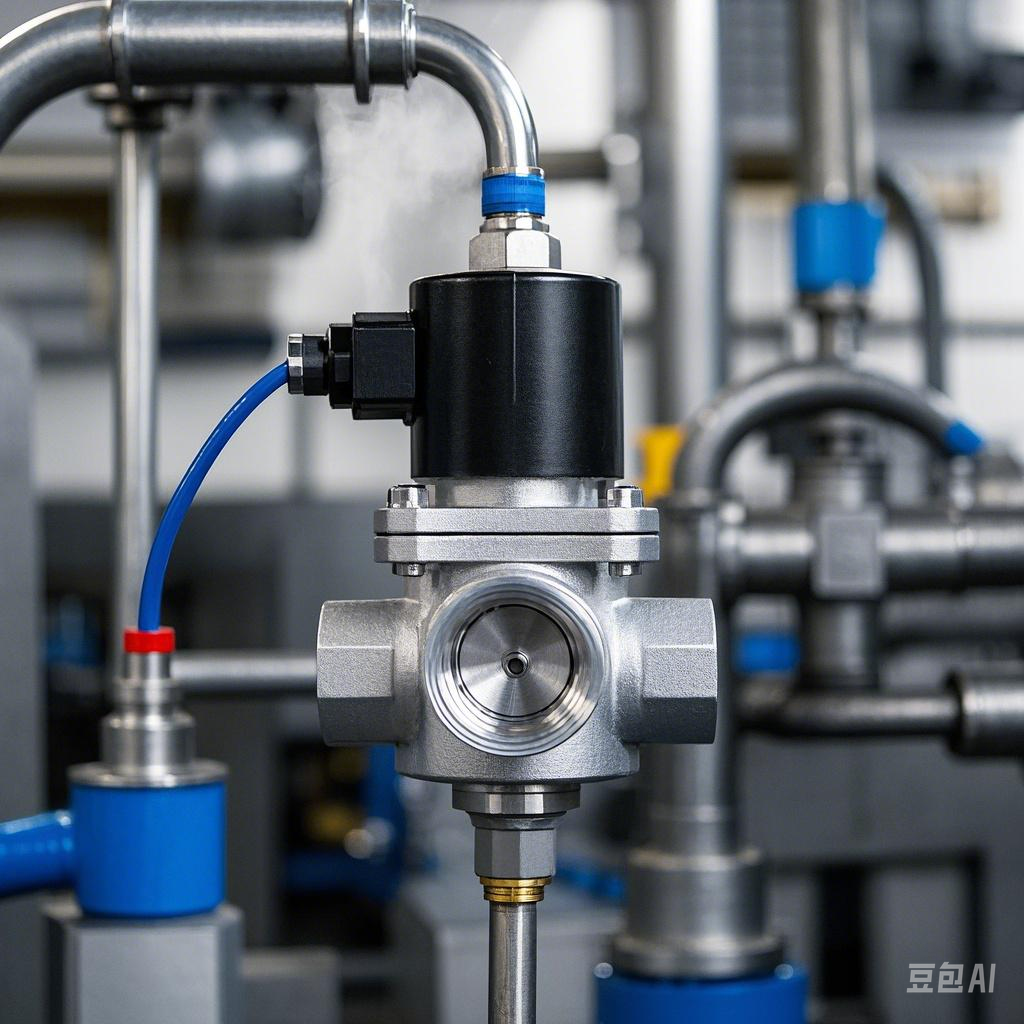
Motorized valves and solenoid valves: key roles in industrial control systems and their differences
In the field of industrial automation, motorized valves and solenoid valves play an indispensable role as important tools for regulating media flow direction, flow rate, speed and other parameters. Although they share similar functions, there are significant differences in performance and application scenarios. This article will provide you with a detailed analysis of the differences between the two, so that you can better understand and select the valve instrumentation to suit your needs.
First, let’s start from the definition. Solenoid valve is actually a special type of electric valve, which uses the magnetic field generated by the solenoid coil to pull the valve spool, thus controlling the opening and closing of the valve. When the coil is de-energized, the spool returns to its initial position by the force of a spring.
In contrast, motorized valves control the opening and closing of the valve by means of an electric actuator. Motorized valves usually consist of two parts: the upper part is the motorized actuator and the lower part is the valve itself. Depending on the actuator, motorized valves can be divided into two types: angle stroke and straight stroke. Angle-stroke motorized valves control the passage of pipeline fluids by rotating up to 90 degrees, while straight-stroke motorized valves achieve the same purpose by moving the valve plate up and down.
In terms of uses and differences, solenoid valves mainly utilize the electromagnetic principle to guide spool movement through the attractive force generated by an energized solenoid coil, and their control mode is usually digital signal (DO) control. Motorized valves, on the other hand, use a reversible electric motor as the driving device to drive the spool through the rotation of the motor to achieve the opening and closing and adjustment of the valve. Electric valves usually use analog signal (AI) control, can more accurately regulate the flow of pipeline media, and in specific environments to support digital signal control.
In the scope of application, solenoid valves are very suitable for use as shut-off valves in pipelines containing corrosive, toxic and other chemical substances due to their excellent anti-leakage properties and fast opening and closing speeds. While the electric valve is more often used for pipeline flow regulation, especially in the air supply refrigeration pipeline, liquid pipeline (such as wine beverage production canning pipeline and sewage pipeline) and other wide range of fields.
In the control mode, the solenoid valve can usually only be used as a switching quantity, suitable for small pipeline control. Motorized valves, on the other hand, are much more flexible and can be used not only as on/off switching but also for analog adjustment. This means that motorized valves can more accurately control the flow of media in the pipeline to meet more complex industrial control needs.
In addition, solenoid valves and motorized valves differ in the nature of their work. Solenoid valves typically have a smaller flow coefficient and a limited operating pressure differential. Motorized valves, on the other hand, are more resistant to voltage shocks and are suitable for high flow rates and pressures. The opening degree of the electric valve can also be controlled, the state includes open, close, half open half closed, etc., so as to realize the precise adjustment of the medium flow in the pipeline.
In terms of applicable technology, solenoid valve is more suitable for some special process requirements, such as high leakage prevention requirements, special fluid media and other occasions. Although the price is relatively high, but its unique performance advantages make the solenoid valve in some specific applications become indispensable choice. Motorized valves are widely used in the field of industrial automation due to its flexible regulation, wide range of applications and other characteristics.
In summary, motorized valves and solenoid valves have their own merits in industrial control systems. Which type of valve instrumentation to choose depends on your specific needs and application scenarios. We hope this article can help you better understand the differences between these two types of valve instrumentation and provide useful reference for your industrial automation projects.
Differences between motorized valves and solenoid valves